Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Suzudo, Tomoaki; Tsuru, Tomohito
no journal, ,
It is important to accurately know the most stable state of self-lattice atoms (SIAs) for the study of irradiated materials. In recent first-principles calculations, SIA dumbbells inclined in the  11h
11h (h
(h  0.5) direction in Mo and W are slightly more stable compared with those in the
0.5) direction in Mo and W are slightly more stable compared with those in the  111
111 direction. However, the difference were small and no clear consensus has been obtained yet. The goal of the current study is to perform highly accurate first-principles calculations for Mo and W to provide the final answer to this problem and to clarify the physical mechanism of the inclination in both metals.
direction. However, the difference were small and no clear consensus has been obtained yet. The goal of the current study is to perform highly accurate first-principles calculations for Mo and W to provide the final answer to this problem and to clarify the physical mechanism of the inclination in both metals.
Tsuru, Tomohito; Lobzenko, I.; Shiihara, Yoshinori*; Wei, D.*; Yamashita, Shinichiro; Itakura, Mitsuhiro; 10 of others*
no journal, ,
High entropy alloys (HEAs) are chemically complex single- or multi-phase alloys with crystal structures. There are no major components but five or more elements are included with near equiatomic fraction. In such a situation, deformation behavior can no longer be described by conventional solid solution strengthening model. Some HEAs, indeed, show higher strengthening behavior and anomalous slip. However, the mechanisms of these features have yet to be understood. Dislocation structure and motion should be the key to identify the unique feature of mechanical properties of HEAs. In the present study, we investigated the core structure of dislocations in body centered cubic (BCC) HEAs using density functional theory (DFT) calculations. The Random structure and ZrNbTaTiHf and the SRO structure obtained from the 800 K MC calculation in two BCC-HEA MoNbTaVW was prepared. Then, the energy distribution when the dislocation dipoles were introduced at 135 sites were calculated. We found that the dislocation formation energy is smaller in ZrNbTaTiHf, which has a large difference in MSAD and a large lattice distortion.
Hamasato, Tsunehiko*; Matsukawa, Yoshitaka*; Tsujimura, Soyo*; Sakaguchi, Chisato*; Tsurekawa, Sadahiro*; Homma, Yoshiya*; Yabuuchi, Kiyohiro*; Yamaguchi, Masatake
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Mori, Hideki*; Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Okumura, Masahiko; Shiihara, Yoshinori*; Matsunaka, Daisuke*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Egusa, Daisuke*; Zhao, Y.*; Saito, Hikaru*; Hata, Satoshi*; Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Abe, Eiji*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 -iron by in situ observation of interstitial clusters using high-voltage electron microscopy
-iron by in situ observation of interstitial clusters using high-voltage electron microscopyAbe, Yosuke; Sato, Yuki*; Hashimoto, Naoyuki*
no journal, ,
Modeling cluster dynamics or rate theory to describe the microstructural evolution of irradiated materials requires a precise knowledge of the migration energies of point defects, i.e. a self-interstitial atom (SIA) and a vacancy, a product of energetic particle radiation. We measured the time evolutions of the number density and size of SIA clusters in electron-irradiated  -iron by in situ observation using high-voltage electron microscopy. By fitting the obtained temperature-dependent quantities to the Arrhenius relations derived by a rate theory analysis, we estimated the point-defect migration energies.
-iron by in situ observation using high-voltage electron microscopy. By fitting the obtained temperature-dependent quantities to the Arrhenius relations derived by a rate theory analysis, we estimated the point-defect migration energies.
Gong, W.; Harjo, S.; Mayama, Tsuyoshi*; Kawasaki, Takuro; Aizawa, Kazuya; Sun, B.*; Tsuji, Nobuhiro*
no journal, ,
In situ neutron diffraction experiments at cryogenic temperature was performed to investigate the temperature dependence of deformation behavior and corresponding activities of deformation mechanisms in a commercial AZ31 Mg alloy. The stress-strain curve at 21K showed slightly higher macroscopic yield stress but remarkably higher fracture stress and strain than that of room temperature. The enhancement of extension twinning and suppression of contraction twinning at cryogenic temperature are considered to be the reasons for improving the corresponding macroscopic strength and ductility in the commercial AZ31 alloy.
 Mg and LPSO of Mg
Mg and LPSO of Mg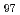 Zn
Zn Y
Y during compression and extrusion ratio
during compression and extrusion ratioHarjo, S.; Aizawa, Kazuya; Gong, W.; Kawasaki, Takuro; Yamasaki, Michiaki*; Kawamura, Yoshihito*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English